The country has been taking focused steps towards achieving energy independence for the last 20-30 years. And this has widened the inclusion of various fuel sources for energy production.
The latest is the addition of geothermal energy to the energy basket. The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has formed an 11-member committee under the aegis of Dr. AK Tripathi. Experts from ONGC Energy Centre, Centre for Earth Sciences and Himalayan Studies, IIT Roorkee, the Geological Survey of India, CSIR, National Geophysical Research Institute are also included in the committee.
Increasing energy demand and the pressure to decarbonize energy generation is one of the key factors that is forcing India to include geothermal energy in its energy basket. This is a big leap in the area of geothermal-based power generation as India has been conducting feasibility studies for decades before mainstreaming it into the power sector. As per the available data, India started its geothermal energy potential assessment in 1972.
Geothermal power generation:
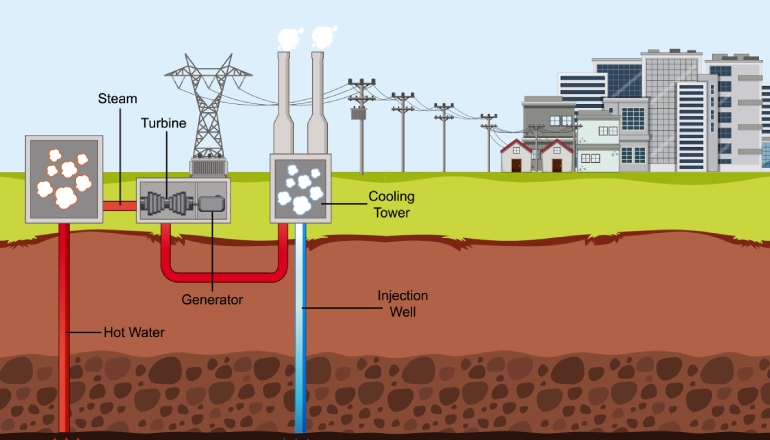
Geothermal energy is the heat energy extracted from the Earth’s crust and is 100 percent renewable. It comes from heat that’s continuously produced deep within the Earth, replenished by the decay of radioactive elements. Wells are drilled into the earth to extract geothermal energy. Geothermal power plants use the heat to produce steam, which turns a turbine that drives generators to create electricity.
Globally, geothermal energy sources are categorized into two; one with high enthalpy geothermal reservoirs and the other with low enthalpy geothermal reservoirs. This division of geothermal reservoirs is based on geological characteristics and temperature of the area. Low enthalpy geothermal reservoirs are potentials with temperatures less than 150 °C, which are found at approximately 1000 m depth. High-temperature geothermal reservoirs have potentials with temperatures more than 200 °C and are found at approximately 1000 m depth. Kenya, Iceland, Italy, New Zealand, Mexico, and the Philippines are some of the other countries working in the field of geothermal energy.
Advantage geothermal:
- Geothermal energy has several advantages over other sources of renewable energy. These include:
- Less environmental damage in comparison to fossil fuel extraction
- Low cost
- Round-the-clock operation
- Firm in nature
- Baseload power
California in the US has the largest geothermal power plant and 85 percent of houses in Iceland are powered by geothermal electricity. As per estimates, India has the potential to generate over 10 GW of geothermal power.
As per the exploration studies, the Geological Survey of India has identified 340 hot springs across the country. The country has low enthalpy geothermal potentials with temperatures ranging from 30 °C to 120 °C. Basis these categories, the potentials have been classified into:
- Northwestern Himalaya
- So-Na-Ta Lineament
- West Coast Margin
- Thermal field of the eastern and northeast region and other geothermal regions
- The Puga geothermal field has the highest enthalpy geothermal water.
The first project is expected to launch in Ladakh. ONGC, the project’s lead agency, anticipates starting the exploration process shortly. If everything goes according to plan, India will have its first geothermal energy by next year.